Epilepsy is a disorder affecting the central nervous system. Patients with epilepsy have abnormal brain activity that can cause seizures or periods of unusual behavior, sensations, and even loss of awareness. The two types of seizures are focal seizures and generalized seizures.
Symptoms of Epilepsy
Patients with epilepsy may experience the following symptoms:
- Temporary confusion
- Stiff muscles
- A staring spell
- Loss of consciousness or awareness
- Uncontrollable jerking movements of the arms and legs
- Psychological symptoms such as anxiety, fear, or deja vu
The types of seizures are focal seizures and generalized seizures.
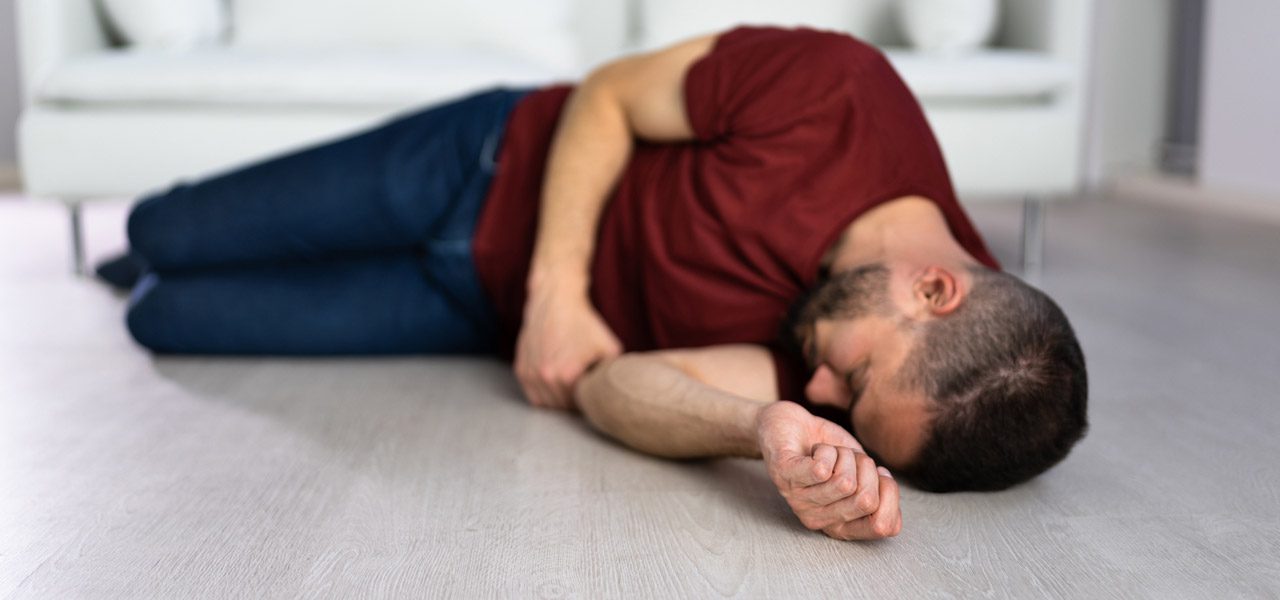

Focal Seizures
A focal seizure may occur without loss of consciousness or with impaired awareness. A focal seizure without loss of consciousness may cause changes in emotions or the way things look, smell, taste, feel, or sound. A seizure may cause involuntary jerking of one body part, such as an arm or leg. Patients may also experience tingling, dizziness, and flashing lights.
A focal seizure with impaired awareness may feel like a dream. Patients undergoing this type of seizure may stare into space and not respond to their environment. They may also perform repetitive motions such as chewing, swallowing, hand rubbing, or walking in circles.
Generalized Seizures
The six types of generalized seizures involve all areas of the brain and include:
- Absence seizures, which are characterized by staring into space with or without subtle body movements, such as lip smacking or eye blinking that last between five and 10 seconds. These seizures may occur up to 100 times per day and cause a brief loss of awareness.
- Tonic seizures cause stiff muscles and may also affect consciousness and muscles in the back, legs, and arms. Some individuals may fall to the ground during a seizure.
- Atonic seizures are also known as drop seizures and may cause loss of muscle control. This type of seizure typically affects the legs and causes patients to suddenly fall or collapse.
- Clonic seizures are associated with rhythmic or repeated jerking muscle movements affecting the face, neck, and arms.
- Myoclonic seizures are characterized by sudden brief jerks or twitches affecting the upper body, arms, and legs.
- Tonic-clonic seizures are the most dramatic type of epileptic seizure and can cause abrupt loss of consciousness, twitching shaking, and body stiffening. Patients may also lose bladder control and bite their tongue.
Diagnosing and Treating Epilepsy
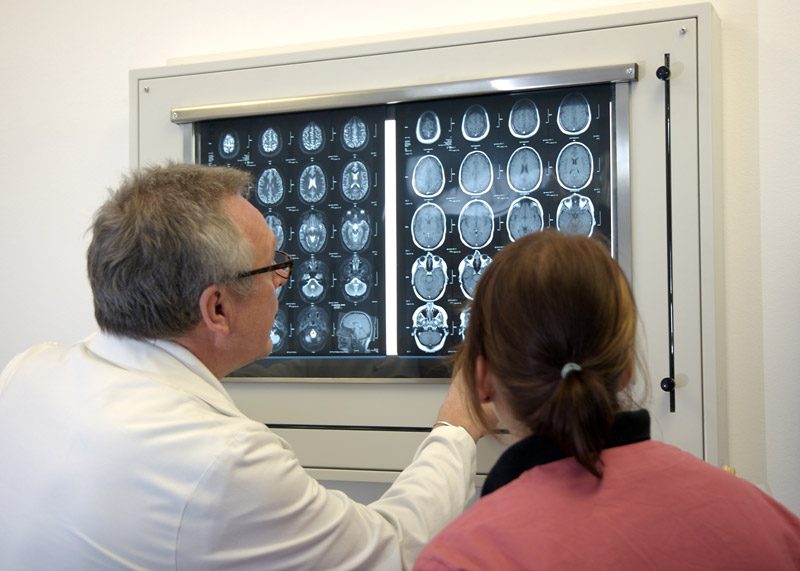
To diagnose a patient’s condition, Dr. Alireza Bozorgi will evaluate the patient’s symptoms and review their medical history. The patient may also undergo a neurological exam that will test their behavior, mental function, and motor abilities to identify the type of epilepsy the patient has. Blood tests may also be done to check for signs of infections, genetic conditions, or other illnesses that may be associated with seizures.
Dr. Bozorgi may also suggest various tests to detect brain abnormalities, such as electroencephalogram (EEG), high-density EEG, computerized tomography (CT) scan, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), function MRI, positron emission tomography (PET), single-photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT), and neuropsychological tests.
Treatment for epilepsy may involve medication, surgery to treat the brain, and various therapies such as vagus nerve stimulation, ketogenic diet, deep brain stimulation, and responsive neurostimulation. Dr. Bozorgi takes a multidisciplinary approach when creating a treatment plan to support full recovery.


